In today’s fast-moving production environments, missing a defect by even seconds can result in thousands of dollars in scrap, extended downtime, or significant regulatory risk. Real-time monitoring for visual inspections has evolved from a luxury into a competitive necessity that defines market leaders across manufacturing, infrastructure, pharmaceuticals, and food production sectors. By leveraging advanced technologies to detect issues instantly, organizations can dramatically improve quality, reduce costs, and enhance compliance.
The Rise of Real-Time Visual Inspection Technologies
Over the past decade, significant advances in camera hardware, machine vision algorithms, deep learning capabilities, and edge computing have revolutionized how organizations approach quality control. These technologies now enable high-accuracy, low-latency visual inspections directly on production floors and in field operations.
Key Market Drivers
- Increasing product complexity and tighter manufacturing tolerances
- Growing regulatory pressure in pharmaceuticals and food safety
- Rising demand for higher uptime and lower operational costs
- Widespread availability of affordable edge devices and cloud services
- Competitive pressure to reduce defect rates and improve quality
According to industry analyses, organizations implementing real-time visual inspection technologies typically see defect rates decrease by 15-30% and experience measurable reductions in downtime. These compelling results are driving significant investment in both on-premises solutions and cloud-based monitoring platforms.
Understanding Real-Time Data Integration for Inspections
Real-time data integration for visual inspections means continuously collecting, processing, and delivering inspection events and telemetry with minimal delay to support instant decision-making. This approach transforms traditional quality control by enabling immediate detection and response to issues.
Core Components of Real-Time Visual Inspection Systems
Data Capture
- High-resolution industrial cameras
- Specialized sensors (thermal, 3D, etc.)
- Environmental monitoring devices
Processing & Analysis
- Edge computing devices for local inference
- AI and machine vision algorithms
- Streaming middleware (MQTT, Kafka)
Presentation & Action
- Real-time dashboards and alerts
- Automated workflow triggers
- Secure storage for compliance
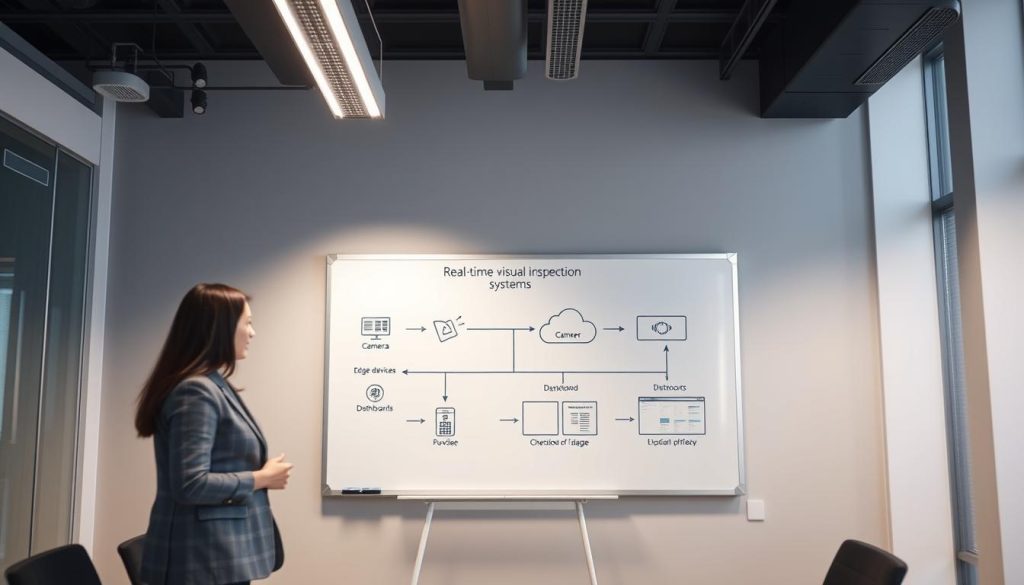
Typical Data Flow in Real-Time Visual Inspection
- Camera captures high-resolution image or video frame
- Edge device preprocesses the image and runs AI model to detect defects
- Defect events with metadata are streamed via MQTT/Kafka to central platform
- Central system correlates events with production records and triggers alerts
- Operators view results in dashboards while automated systems initiate responses
- Full-resolution images are securely archived for compliance and analysis
Example event payload for a detected defect:
{
"timestamp": "2025-06-01T13:42:10Z",
"camera_id": "line3_cam2",
"image_url": "s3://bucket/inspection/2025-06-01/line3_cam2_134210.jpg",
"defect_type": "scratch",
"confidence": 0.93,
"unit_id": "SN123456",
"action": "hold_and_notify"
}
Key Benefits of Real-Time Inspection Data
Faster Defect Detection
Real-time visual inspection dramatically reduces the gap between defect occurrence and detection, allowing for immediate corrective action. Organizations typically report 50-80% reductions in Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) after implementation.
Enhanced Compliance
For regulated industries, real-time inspection systems create time-stamped, image-backed audit trails that simplify regulatory submissions and investigations, helping meet standards like ISO 9001 and FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
Operational Efficiency
Beyond defect detection, real-time inspection data drives operational improvements through early warning for equipment wear, optimization of downstream processes, and reduced labor costs for manual inspection.
Transform Your Quality Control Process
Discover how our real-time monitoring solutions can help you reduce defects, improve compliance, and optimize operations.
Request a Free Consultation
Real-Time Visual Inspection Technologies and Tools
The effectiveness of real-time monitoring solutions for visual inspections depends on selecting the right combination of hardware, software, and integration approaches. Modern systems leverage multiple technologies to achieve optimal results.
Camera Systems and Machine Vision
- High-resolution industrial cameras: Capture detailed images for precise defect detection
- Line-scan cameras: Ideal for continuous web processes and high-speed production
- Thermal cameras: Detect temperature-based anomalies invisible to standard cameras
- 3D/depth cameras: Measure dimensional accuracy and surface variations
- Multi-spectral imaging: Identify defects across different light wavelengths
AI-Based Image Analysis
Modern visual inspection systems leverage sophisticated AI algorithms to detect and classify defects with unprecedented accuracy. These approaches have largely replaced traditional rule-based systems for complex inspection tasks.
| AI Technology |
Application |
Benefits |
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) |
General defect detection and classification |
High accuracy for visual pattern recognition |
| Transfer Learning |
Training with limited defect samples |
Requires fewer training images |
| Instance Segmentation |
Precise defect localization |
Identifies exact defect boundaries |
| Anomaly Detection |
Finding novel or rare defects |
Detects previously unseen issues |
| Optical Character Recognition (OCR) |
Label verification and code reading |
Ensures correct product identification |
Edge Computing and Cloud Integration
Cloud-Based Solutions
- Scalable resources for complex analytics
- Centralized management across multiple sites
- Simplified remote access and monitoring
- Automatic updates and maintenance
Edge-Based Solutions
- Ultra-low latency for real-time decisions
- Operates during network interruptions
- Reduced bandwidth costs and requirements
- Enhanced data privacy and security
Most effective implementations use a hybrid approach, combining edge computing for low-latency detection with cloud integration for analytics, storage, and cross-site coordination. This balanced architecture delivers both the immediacy required for production control and the analytical depth needed for continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Implementing Real-Time Visual Inspection
Designing an Effective Strategy
- Define clear objectives: Establish specific goals such as reducing defect escape rates, shortening MTTR, or meeting regulatory requirements
- Prioritize inspection points: Focus initial efforts on areas with the highest cost-of-failure or quality impact
- Implement staged rollout: Start with a pilot, refine based on results, then scale to additional areas
- Set performance criteria: Define acceptance thresholds for model accuracy (precision/recall) and system latency
- Develop a dataset strategy: Create processes for collecting, labeling, and managing training images
Data Governance and Security
Effective real-time visual inspection systems require robust data governance and security practices to ensure both performance and compliance.
Key Governance Practices
- Implement role-based access controls for inspection data
- Maintain complete data lineage for regulatory compliance
- Create immutable audit logs for all system actions
- Establish data retention policies balancing needs and costs
- Develop model validation and retraining procedures
Security Considerations
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest
- Secure camera networks from unauthorized access
- Implement secure boot and signed firmware for edge devices
- Conduct regular security assessments and updates
- Create incident response plans for security events
Pro Tip: Reference industry standards like ISO 9001 for quality management, NIST guidelines for IoT security, and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records when designing your governance framework.
Implementation Considerations and Integration Patterns
Successfully deploying real-time monitoring solutions for visual inspections requires careful consideration of integration patterns, system architecture, and vendor selection criteria.
Integration with Existing Systems
Real-time inspection systems must seamlessly connect with existing manufacturing and enterprise systems to deliver maximum value. Common integration points include:
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): For production tracking and quality holds
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): For inventory and quality cost accounting
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): For design feedback and specification verification
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): For routing and disposition of inspected items
- Quality Management Systems (QMS): For non-conformance management and CAPA
Architecture Considerations
Latency Requirements
For time-critical inspections, perform inference directly on edge devices to achieve millisecond-level response times without network dependencies.
Bandwidth Management
Implement adaptive sampling and selective transmission strategies to reduce network load while maintaining inspection coverage.
Resilience Planning
Design systems with local buffering and offline capabilities to maintain operation during network or cloud outages.
Vendor Selection Criteria
| Criteria |
Questions to Ask |
Importance |
| Model Accuracy |
What precision/recall can be achieved on our specific defect types? |
Critical |
| Performance |
What is the inference latency and throughput on target hardware? |
High |
| Integration |
Which protocols and APIs are supported for MES/ERP connection? |
High |
| Security |
How is data encrypted, and what access controls are available? |
Critical |
| Lifecycle |
What is the process for model retraining and performance monitoring? |
Medium |
| TCO |
What are the hardware, licensing, and maintenance costs? |
High |
| Support |
What SLAs are offered for technical support and updates? |
Medium |
Need Help Selecting the Right Solution?
Our experts can help you evaluate options and design a real-time visual inspection system tailored to your specific requirements.
Schedule a Consultation
Case Studies: Real-Time Visual Inspection in Action
Manufacturing: Automotive Components
Challenge
A tier-one automotive supplier needed to improve detection of surface defects on machined components while increasing production throughput.
Solution
Implemented a real-time visual inspection system using line-scan cameras and CNN-based defect detection models deployed on edge computing devices. The system integrated directly with their MES to automatically route defective parts to rework stations.
Results
- Defect detection accuracy improved to 98% (precision 0.96 / recall 0.97)
- Production throughput increased by 12% due to reduced manual inspection
- Mean Time to Repair for tooling issues reduced by 45% through early detection
- Annual savings of $1.2M from reduced scrap and warranty claims
Infrastructure: Power Transmission
Challenge
A utilities provider needed to improve monitoring of critical transmission infrastructure to prevent failures and reduce outage times.
Solution
Deployed thermal and visual cameras on substations and transmission lines with edge AI for anomaly detection. The system used a hybrid architecture with edge processing for immediate alerts and cloud integration for historical analysis and predictive maintenance.
Results
- Identified 23 potential failure points before they caused outages
- Reduced average outage response time by 37%
- Improved maintenance planning with data-driven prioritization
- Achieved ROI within 14 months through prevented outages
Pharmaceuticals: Packaging Verification
Challenge
A pharmaceutical manufacturer needed to ensure 100% inspection of packaging integrity, label placement, and product verification while maintaining compliance with FDA regulations.
Solution
Implemented a multi-camera inspection system with specialized AI models for seal verification, OCR for label reading, and barcode validation. The system maintained a complete audit trail with time-stamped images and operator verifications.
Results
- Achieved zero defect escapes in packaging integrity
- Reduced batch release time by 40% through automated verification
- Simplified FDA audits with comprehensive electronic records
- Eliminated manual inspection costs while improving reliability
Getting Started with Real-Time Visual Inspection
Implementation Checklist
Phase 1: Planning
- Define specific objectives and success metrics
- Identify high-priority inspection points
- Document current defect types and inspection processes
- Assess existing infrastructure and integration points
- Develop preliminary ROI model and budget
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation
- Select initial inspection point for proof of concept
- Choose hardware and software components
- Collect and label sample images for training
- Configure integration with existing systems
- Train operators and establish new workflows
Phase 3: Evaluation
- Measure system performance against objectives
- Gather feedback from operators and stakeholders
- Identify improvement opportunities
- Refine integration and workflows
- Update ROI model with actual results
Phase 4: Scale-Up
- Develop rollout plan for additional inspection points
- Standardize deployment process and documentation
- Implement governance and maintenance procedures
- Train additional personnel as needed
- Establish continuous improvement process
Ready to Transform Your Visual Inspection Process?
Our team of experts can help you design, implement, and optimize real-time monitoring solutions tailored to your specific requirements.
Request Your Free Proof of Concept
Real-time monitoring solutions for visual inspections represent a significant advancement in quality control and operational efficiency. By combining advanced camera systems, AI-based image analysis, and seamless integration with manufacturing systems, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of defect detection while reducing costs and improving compliance. Whether you’re in manufacturing, infrastructure management, pharmaceuticals, or food production, implementing these technologies can provide a substantial competitive advantage in today’s quality-driven marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What ROI can we expect from implementing real-time visual inspection?
ROI varies by industry and application, but most organizations see payback periods of 6-18 months. Key value drivers include reduced scrap and rework costs, decreased warranty claims, improved production throughput, and reduced labor costs for manual inspection. For critical applications, preventing even a single major quality escape can justify the entire system investment.
How much training data is needed for effective AI-based inspection?
The amount of training data required depends on defect complexity and variability. Simple defect detection may require only 50-100 labeled examples per defect type, while complex classification tasks might need 500+ examples. Modern approaches like transfer learning and data augmentation can significantly reduce these requirements. Many vendors offer pre-trained models that can be fine-tuned with smaller datasets.
Can real-time visual inspection systems integrate with our existing quality management system?
Yes, modern visual inspection platforms are designed to integrate with existing systems through standard protocols and APIs. Common integration points include REST APIs, MQTT, OPC-UA, and database connections. Most vendors provide pre-built connectors for popular MES, ERP, and QMS platforms. Custom integrations can typically be developed for specialized or legacy systems.
How do we ensure our visual inspection system remains compliant with regulations?
Regulatory compliance requires attention to several key areas: data integrity, access controls, audit trails, and validation. Look for systems that provide immutable records, role-based access, comprehensive logging, and validation documentation. For FDA-regulated industries, ensure the system supports 21 CFR Part 11 compliance with features like electronic signatures and record retention. Regular system audits and documentation updates are essential for maintaining compliance.